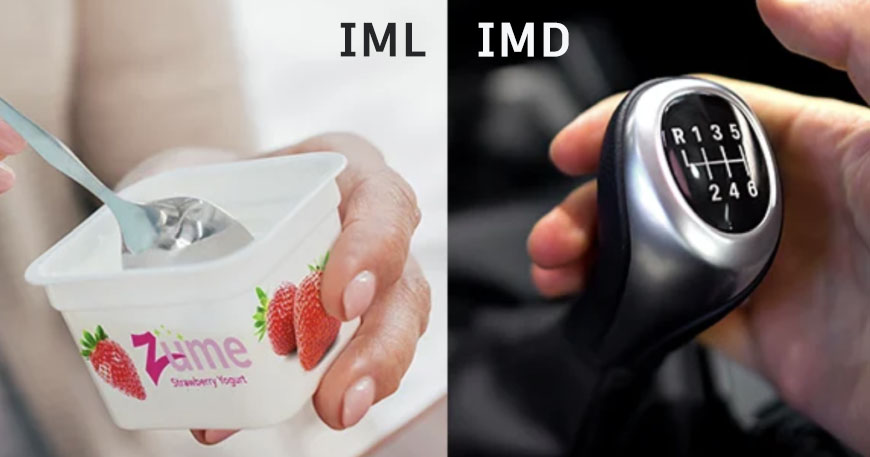
In injection molding, aesthetics, functionality, and durability are critical in achieving high-quality parts. Two advanced techniques used to decorate and enhance the appearance of molded parts are IMD (In-Mold Decoration) and IML (In-Mold Labeling). These methods are widely used in various industries such as automotive, consumer electronics, packaging, and home appliances to integrate decorative and functional features directly into molded parts during the molding process.
In this article, we will explore the differences between IMD and IML, how each process works, their advantages, and which one is best suited for specific applications.

What is In-Mold Decoration (IMD)?
In-Mold Decoration (IMD) is a process where a decorative film or label is placed inside the mold cavity before injection molding. During the molding process, the film or label is fused with the part as it is molded, creating a durable, scratch-resistant design that becomes part of the surface of the molded part. IMD is commonly used for high-end products like automotive interiors, home appliances, and consumer electronics.
How IMD Works:
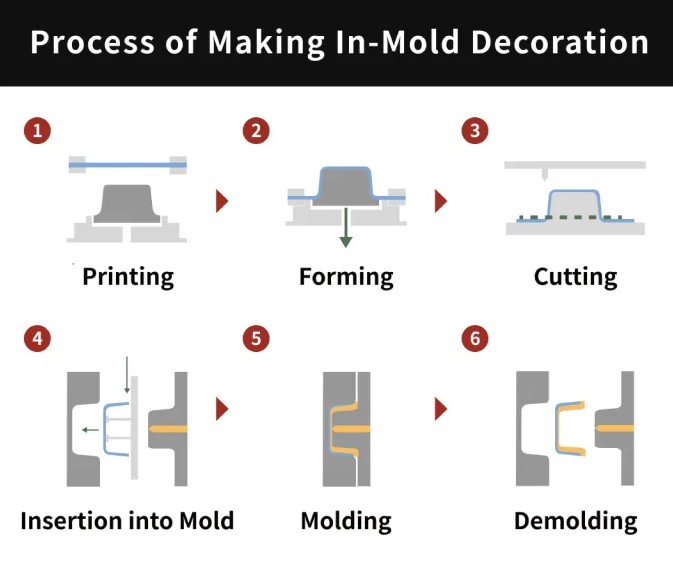
1.A decorative film or graphic (typically made from polyester, polycarbonate, or other plastic films) is placed inside the mold cavity.
2.The mold is closed, and the plastic material is injected into the cavity, fusing the film or label to the surface of the part.
3.The part cools and solidifies, with the decorative film now permanently integrated into the surface of the molded part.
Advantages of IMD:
- Durability: The decoration becomes a permanent part of the product, making it resistant to wear, scratching, and fading.
- Design Flexibility: IMD allows for complex designs, including textures, colors, and patterns, providing a high-quality finish.
- Cost-Effective for High Volumes: Once the mold is designed, IMD is ideal for high-volume production, making it cost-efficient for mass-produced products.
- High-Quality Finish: IMD provides a sleek, high-gloss finish, making it ideal for products that require an aesthetic, premium look.
Applications of IMD:
- Automotive interiors (e.g., dashboards, control panels)
- Home appliances (e.g., refrigerator panels, microwave bezels)
- Consumer electronics (e.g., smartphones, gaming consoles)
- Decorative parts for the fashion and packaging industries.

What is In-Mold Labeling (IML)?
In-Mold Labeling (IML) is a technique where pre-printed labels are placed into the mold cavity before the injection molding process. The label typically has adhesive backing or is designed to bond chemically with the molten plastic during the molding process. IML is primarily used for packaging, food containers, and consumer products.
How IML Works:
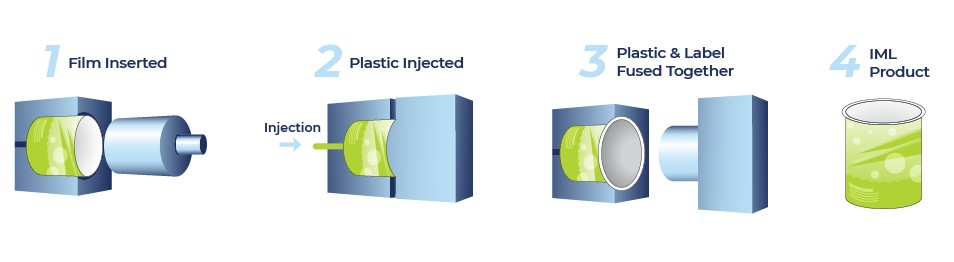
1.A pre-printed label, often made from materials such as polypropylene (PP), is inserted into the mold cavity. The label is typically printed with designs, logos, or product information before being placed inside the mold.
2.During the molding cycle, molten plastic is injected into the mold, and the label bonds with the surface of the part as it cools.
3.The part is ejected with the label permanently adhered to its surface, creating a smooth, seamless finish.
Advantages of IML:
- High-Quality Graphics: IML allows for high-resolution graphics, including intricate designs and detailed logos, that are directly integrated into the molded part.
- Durability: The label is not just adhered to the surface but becomes an integral part of the molded product, offering resistance to peeling, fading, and abrasion.
- Product Branding: IML is particularly popular in consumer goods and packaging where branding and product information need to be prominently displayed.
- Cost-Effective for Medium to High Volumes: IML is well-suited for medium to high-volume production runs, offering a good balance between cost and quality.
Applications of IML:
- Packaging (e.g., yogurt cups, food containers, cosmetic packaging)
- Consumer goods (e.g., bottles, containers)
- Household products (e.g., plastic bins, kitchenware)
- Pharmaceutical and chemical packaging.
IMD vs IML: Key Differences
While both IMD and IML are in-mold decoration techniques that integrate graphics or labels directly into molded parts, they have distinct differences in their processes, materials, and typical applications. Below is a comparison of the two:
| Feature | In-Mold Decoration (IMD) | In-Mold Labeling (IML) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Used | Decorative film (polycarbonate, polyester) | Pre-printed labels (typically polypropylene) |
| Surface Integration | Decorative film is fused into the surface of the molded part | Label bonds chemically with the part during molding |
| Applications | Automotive, electronics, home appliances | Packaging, food containers, consumer products |
| Durability | Scratch-resistant, high durability | Resistant to peeling, fading, and abrasion |
| Graphic Quality | High-quality, intricate designs, textures | High-resolution graphics and branding |
| Process Complexity | More complex, requires precise film placement | Simpler process with pre-printed labels |
| Cost-Efficiency for Volumes | Best for high-volume production | Cost-effective for medium to high-volume production |
| Flexibility | Suitable for complex surface textures | Ideal for product labeling, branding, and packaging |
| Finish Quality | High-gloss, premium finish | Smooth, seamless integration |
Choosing Between IMD and IML
The choice between IMD and IML depends on the specific requirements of the part being produced, including design complexity, application, material requirements, and production volume. Here’s how to decide which method is best for your project:
Choose IMD if:
- You need a high-end, premium look with complex textures or intricate designs.
- The product requires durability, such as resistance to scratches, fading, or wear.
- You are producing automotive or consumer electronics parts that demand high-quality finishes.
- You are manufacturing in high volumes and need cost-efficiency.
Choose IML if:
- You need to label products, such as containers or packaging, with clear branding and product information.
- You need high-quality graphics but with simpler design elements than those typically achievable with IMD.
- The primary goal is functional labeling, particularly in the food and beverage industry.
- Your production volumes are medium to high, and you want a cost-effective solution for labeling.
Both IMD (In-Mold Decoration) and IML (In-Mold Labeling) are innovative processes in injection molding that allow manufacturers to create visually appealing, functional, and durable parts. The key difference lies in the type of decoration used—IMD incorporates decorative films for premium, high-end finishes, while IML uses pre-printed labels, ideal for product branding and packaging.
Choosing between IMD and IML ultimately depends on the specific application, required durability, and production volume. Understanding these two techniques will help you select the right method for your injection molding projects, optimizing both cost-efficiency and product quality.











