SYNOR’s basic guidelines for overmolding and insert molding include important design considerations to help improve part manufacturability, enhance cosmetic appearance, and reduce overall production time.
Size
Maximum Dimensions

| IN | MM | |
| SIZE | 18.9 in. x 29.6 in. x 8 in. | 480mm x 751.8mm x 203.2mm |
| VOLUME | 59 cu. in. | 966837 cu. mm |
| DEPTH | 4 in. from parting line | 101mm from parting line |
| Up to 8 in. if the parting line can pass through the middle of the part | Up to 203.2mm if the parting line can pass through the middle of the part | |
| PROJECTED MOLD AREA | 175 sq. in. (plastic) | 112903 sq. mm (plastic) |
| 48 sq. in. (silicone rubber) | 30968 sq. mm (silicone rubber) |
Height may be limited if using a silicone as the overmold material, and deeper parts are limited to a smaller outline. Minimum part volume is 0.025 cu. in. (40.98 cu. mm). With substrate molds, we can maintain a machining tolerance of ±0.003 in. (0.08mm) with an included resin tolerance that can be greater but no less than 0.002 in./in. (0.002mm/mm). With thermoplastic overmolds, tolerances remain the same as substrate molds, however, if the overmold is LSR, then tolerances shift to 0.025 in./in. (0.025mm).
Insert Molding Capabilities
Instead of a mold that produces a final part using two separate shots like overmolding, insert molding generally consists of a preformed part—often metal—that is loaded into a mold, where it is then overmolded with plastic to create a part with improved functional or mechanical properties. We currently accept inserts from PEM, Dodge, Tri-Star, Spirol, and Tappex. A complete chart of stocked inserts at SYNOR is available here.
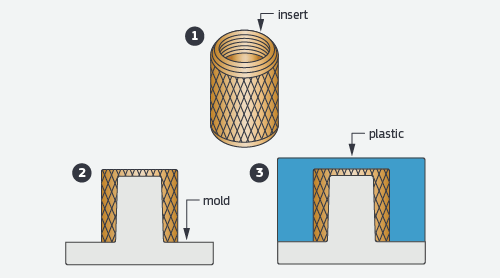
A threaded insert is placed atop a mold core where plastic is molded over it to form the final component.
One way insert molding is used is with threaded inserts, which reinforce the mechanical properties of plastic parts’ ability to be fastened together, especially over repeated assembly. Bushings and sleeves are another great way to increase part durability for mating components that need more abrasion resistance due to moving parts.
Materials

| ABS | PPS |
| Acetal | PS |
| HDPE | PS |
| LCP | PSU |
| PEI | TPE |
| PMMA | TPU |
| Polycarbonate | PEEK |
| Polypropylene | Liquid Silicone Rubber |
| PPA |
Overmolding Material Bonding
Chemical bonding between overmolded materials is possible, but material compatibility should be considered in order to achieve desired bond strength. Incorporation of an adequate mechanical bond is strongly recommended if bonding is critical to your application. An undercut is a good example of a mechanical bond.

| Substrate Material | |||||
| Overmold Material | ABS Lustran | ABS/PC CYCOLOY C2950-111 | PC Lexan | PBT Valox | PP Profax 6323 |
| 940-701 | 357-1001 | ||||
| TPU – Texin 983-000000 | C | C | C | C | M |
| TPV – Santoprene 101-87 | M | M | M | M | C |
| TPE – Santoprene 101-64 | M | M | M | M | C |
| LSR – Elastosil 3003/30 A/B | – | – | M | M | – |
| TPC – Hytrel 3078 | C | C | C | C | M |
| TPE-Versaflex OM 1060X-1 | C | C | C | M | M |
| TPE-Versaflex OM 6240-1 | M | M | M | M | M |
| TPE-Versaflex OM 6258-1 | M | M | M | M | M |
| TPE-Versaflex OM 1040X-1 | C | C | C | M | M |
M = mechanical bond (recommended), C = chemical bond
Surface Finishes
| FINISH | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| PM-F0 | non-cosmetic, finish to Protolabs’ discretion |
| PM-F1 | low-cosmetic, most toolmarks removed |
| PM-F2 | non-cosmetic, EDM permissible |
| SPI-C1 | 600 grit stone, 10-12 Ra |
| PM-T1 | SPI-C1 + light bead blast |
| PM-T2 | SPI-C1 + medium bead blast |
| SPI-B1 | 600 grit paper, 2-3 Ra |
| SPI-A2 | grade #2 diamond buff, 1-2 Ra |
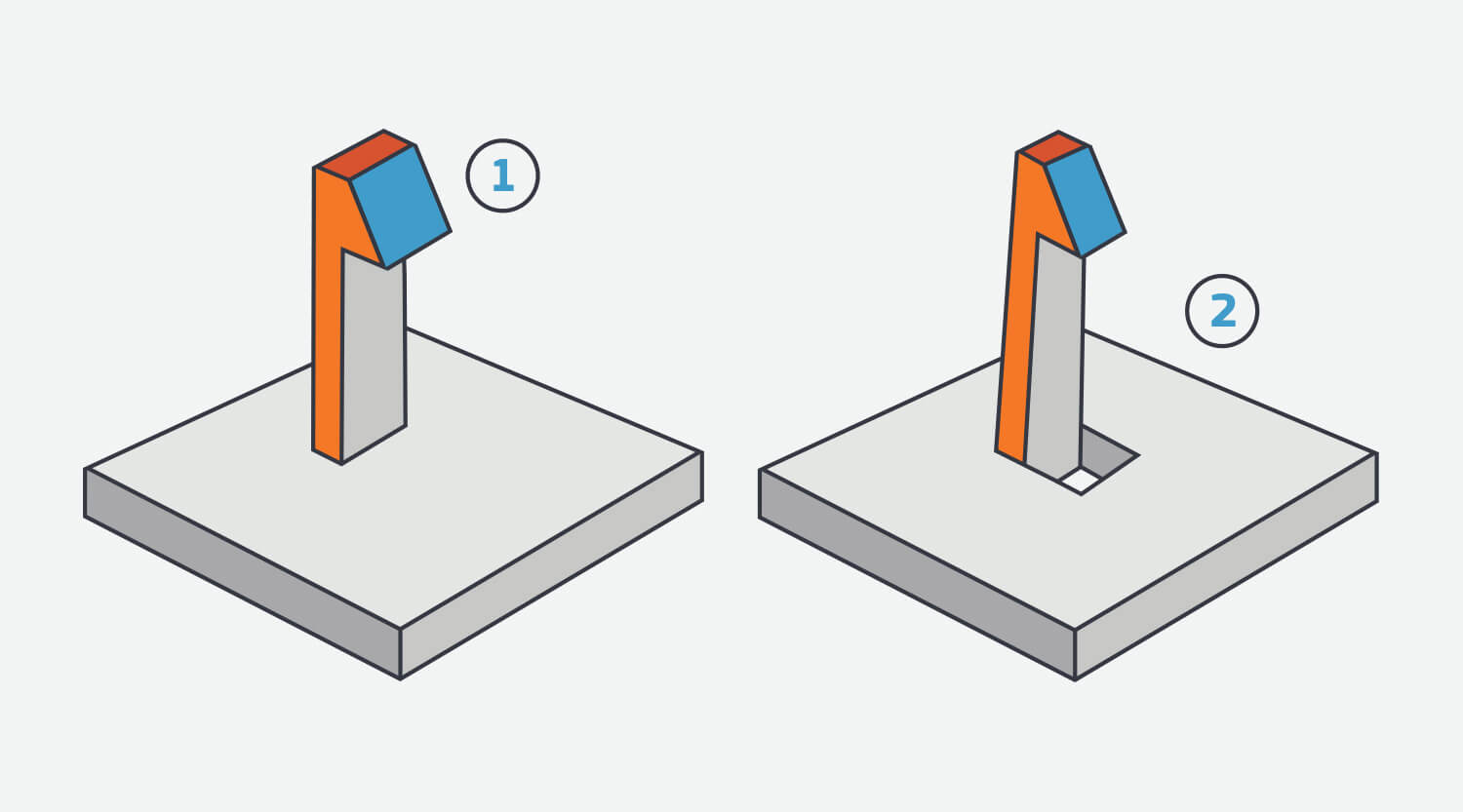
Draft
Adding draft angles to design helps facilitate ejection of a part from a mold, and improves overall moldability.
| VERTICAL FACES | 0.5° |
|---|---|
| MOST SITUATIONS | 2° |
| MINIMUM FOR SHUT OFF | 3° |
| MINIMUM FOR LIGHT TEXTURE (PM-T1) | 3° |
| MINIMUM FOR LIGHT TEXTURE (PM-T2) | 5°+ |
Undercuts
Maximum Side Core Dimensions
| WIDTH | HEIGHT | PULL | |
| IN | < 8.419 in. | < 2.377 in. | < 2.900 in. |
| MM | <213.84mm | <60.38mm | <73.66mm |
Wall Thickness
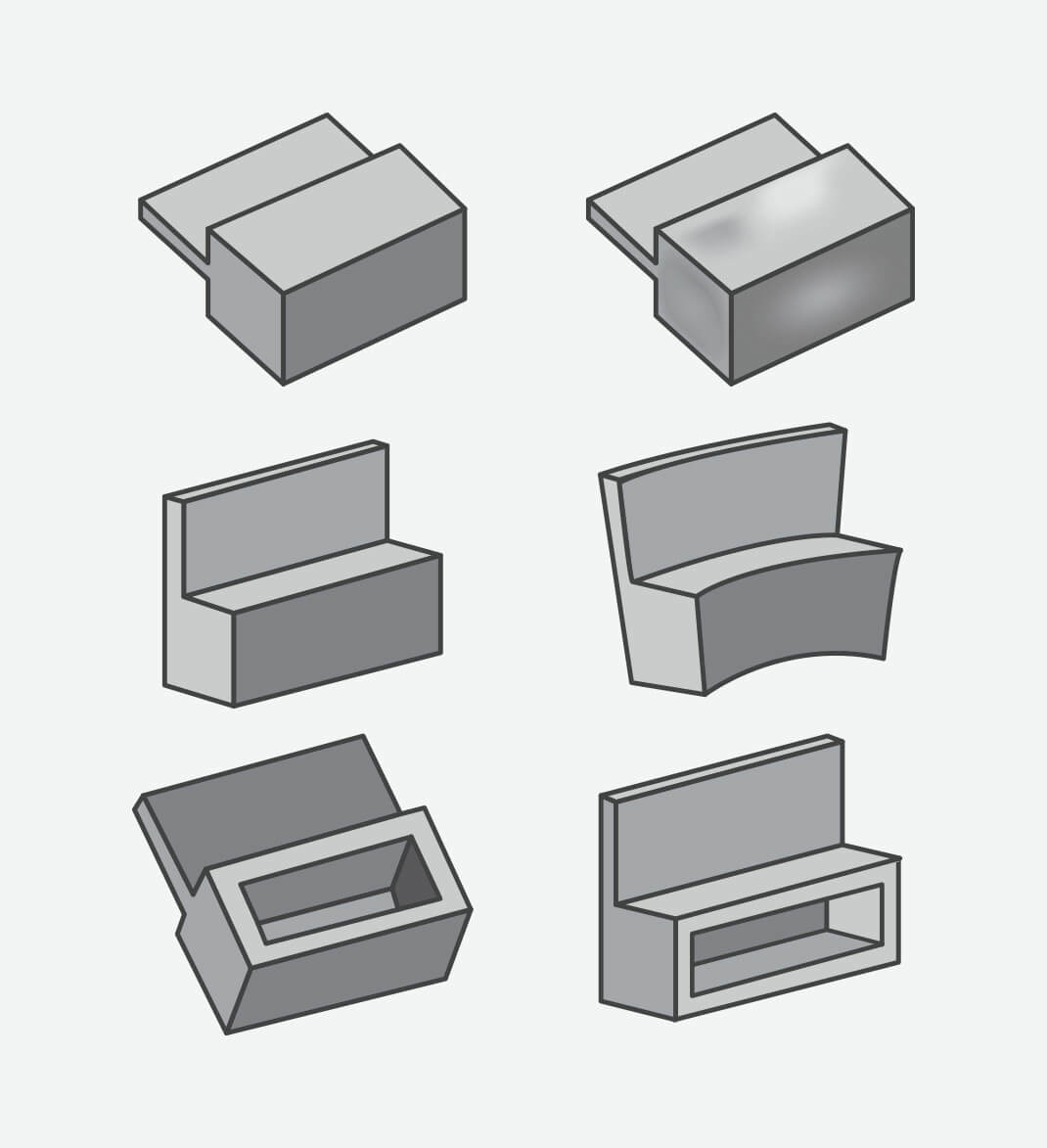
The top row represents a part designed with thick features and the resulting sink once molded. The middle row also shows a part designed with thick features, but this time the warp that occurs once molded. The bottom row demonstrates how coring out thick features helps create an optimally molded part.
| MATERIAL | RECOMMENDED WALL THICKNESS | |
| IN | MM | |
| ABS | 0.045 in. – 0.140 in. | 1.143mm – 3.556mm |
| Acetal | 0.030 in. – 0.120 in. | 0.762mm – 3.048mm |
| Acrylic | 0.025 in. – 0.500 in. | 0.635mm – 12.7mm |
| Liquid Crystal Polymer | 0.030 in. – 0.120 in. | 0.762mm – 3.048mm |
| Long-Fiber Reinforced Plastics | 0.075 in. – 1.000 in. | 1.905mm – 25.4mm |
| Nylon | 0.030 in. – 0.115 in. | 0.762mm – 2.921mm |
| Polycarbonate | 0.040 in. – 0.150 in. | 1.1016mm – 3.81mm |
| Polyester | 0.025 in. – 0.125 in. | 0.635mm – 3.175mm |
| Polyethylene | 0.030 in. – 0.200 in. | 0.0762mm – 5.08mm |
| Polyphenylene Sulfide | 0.020 in. – 0.180 in. | 0.508mm – 4.572mm |
| Polypropylene | 0.035 in. – 0.150 in. | 0.635mm – 3.81mm |
| Polystynene | 0.035 in. – 0.150 in. | 0.89mm – 3.81mm |
| Polyurethane | 0.080 in. – 0.750 in. | 2.032mm – 19.05mm |
Radii
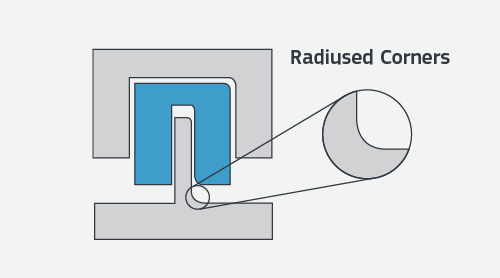
Some part corners will have a radius rather than a sharp edge since we use an automated CNC milling process to make the mold for your parts. This typically does not require a change to your model, but resulting radii are identified before the mold is milled.










